If you are a managed service provider (MSP) handling small and medium-sized businesses (SMB) clients, there are some sobering stats you need to be aware of. For example, 50% of small to medium-sized businesses have been the victims of cyber attacks, and over 60% of those attacked go out of business.
In 2024, no single company can claim they are too small or insignificant to be the victim of a cyber hack. And that’s why every MSP needs to quickly familiarize themselves with SMB hack remediation.
In this post, we’ll rundown some of the common methods attackers use to gain access to an SMB’s system. Then, we’ll walkthrough some of the different ways you can clean up the mess and secure your client’s environment.
How are SMB’s hacked?
One common attack method is the SMB relay attack. This has nothing to do with being an SMB as we previously defined it, but rather with the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol—a common file-sharing protocol used in Windows environments—particularly in small and medium businesses (SMBs). SMB is a client-server protocol operating at the application layer of the network protocol stack.
During a relay attack, an attacker intercepts and relays messages between the client and the SMB server, potentially gaining unauthorized access to sensitive data. This attack can be particularly effective on outdated systems such as Windows XP or Windows Server 2003, which may have unpatched SMB vulnerabilities.
Exploits and malicious code, often delivered through techniques like phishing attacks on the machine or through the exploitation of other vulnerabilities, can compromise the target client machine. Once access is gained, attackers may use a variety of methods, including the use of Python scripts or remote shells, to execute malicious actions on the target system.
Brute force attacks may also be employed to crack weak passwords, emphasizing the importance of strong passwords to prevent unauthorized access. EternalBlue, a notorious exploit targeting Windows Vista systems, exemplifies the severity of SMB-related vulnerabilities and emphasizes the need for robust security practices.
How do you remediate an SMB hack?
The process of remediating a hack involves a series of steps to identify, contain, and remove the malicious actors and restore the affected systems to a secure state. Remediation is a complex and time-consuming process that requires specialized expertise and resources, so don’t be afraid to ask for help. In severe cases, it may be necessary to engage professional cybersecurity services to assist with the investigation, eradication, and recovery phases.
Of course, prevention is always better than a cure. Security measures to counter SMB-related cyber threats include regularly patching and updating operating systems to address vulnerabilities, employing strong passwords, and restricting access to shared folders.
Additionally, monitoring network activity, detecting and blocking malicious files, and securing open ports are crucial steps in preventing unauthorized access.
Post-exploitation activities may involve the exfiltration of sensitive data, such as user credentials or company files, potentially leading to severe consequences for the targeted organization.
Resolving a hack in five steps
In the aftermath of a hack, swift and effective action is crucial to contain the damage, restore affected systems, and prevent future breaches. The remediation process involves a series of coordinated steps that address the immediate threat, investigate the root cause, and implement long-term security improvements.
1. Find the Risks
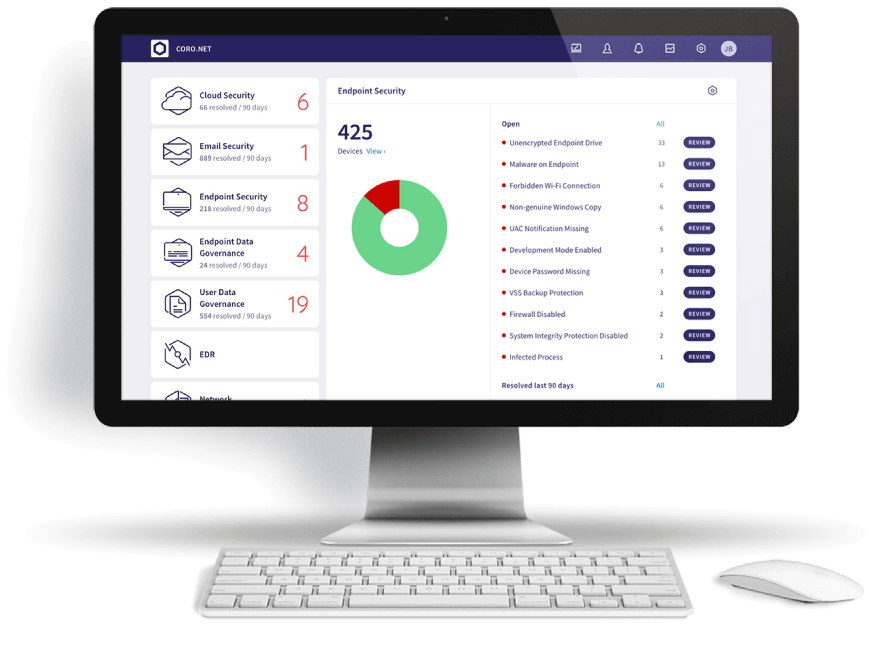
Preferably before a hack occurs, you have to know where the risks are by auditing the IT infrastructure of the entire organization. Make a list of your computer systems, servers, internal network, mobile devices, and data storage, and assign risks to each system. Then, identify threats to each system. Your risk assessment should include:
- A scan of all devices connected to the network: This scan should include laptops, smartphones, printers, and any other devices that can access the network. It should also look for unauthorized devices that may have been connected to the network without permission.
- A review of antivirus standards and how they’re being implemented: Ensure that all devices are protected with up-to-date antivirus software and that all settings are configured to detect and block malware.
- Revisiting the patching process: Software vulnerabilities are often discovered and exploited by attackers before they are patched. A proactive review of the patching process should ensure that critical patches are being applied in a timely manner. This may involve implementing a patch management system that automatically scans for and installs patches.
- Checking all configurations for wireless networks, including passwords and encryption standards: Wireless networks are often used by employees to access sensitive data. A review of all configurations for wireless networks should ensure that they are using strong passwords and encryption standards to protect against unauthorized access.
- An assessment of user behavior: This should include how employees are using email and the internet. Employees can be a major source of risk to an organization’s security. An assessment of user behavior should identify any potential risks, such as employees clicking on phishing links or opening unknown attachments.
2. Look for Solutions
Following a hack, there are several remedies you could implement, from making sure that you are installing patches in a timely manner to a complete overhaul of your security system. Remedies could include:
- Patch management: A critical cybersecurity practice that involves identifying, evaluating, and applying software updates to address vulnerabilities in systems and applications. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access, steal sensitive data, or disrupt operations. A comprehensive patch management program can significantly reduce an organization’s risk of cyberattacks.
- Data loss prevention (DLP): A set of technologies and procedures aimed at preventing sensitive data from being stolen, leaked, or accidentally exposed. Sensitive data can include personally identifiable information (PII), financial information, intellectual property, and other confidential assets.
- Firewall configuration: A firewall acts as a gatekeeper for network traffic, monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing communication. It can block unauthorized access, filter out malicious traffic, and protect against network-based attacks.
- Antivirus software: Antivirus software is designed to detect and remove malware, a broad term encompassing malicious software that can harm systems, steal data, or disrupt operations.
- Secure remote access: Secure remote access enables authorized users to access corporate systems and resources from remote locations. It is crucial to implement strong security measures to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
- Strong passwords: Strong passwords are complex and difficult to guess, reducing the risk of unauthorized account access and data breaches.
These simple remedies will go a long way in protecting your client from hackers.
3. Monitor Everything
A monitoring program is the backbone of the remediation, especially after you are done with applying the necessary solutions. There are two key reasons why this is important. First, you need to make sure that all priority threats have been completely eliminated and that your systems are safe and sound. Second, it helps you understand how well the current security measures are working and what needs to be improved.
Start by establishing a baseline of normal activity for your systems. This will help you quickly identify anything that’s out of the ordinary. The monitoring program should also include alerts for any changes or abnormalities. This will help you catch things early before they have a chance to cause damage.
In order to establish a baseline, you can use a variety of tools and techniques, such as:
- Network traffic monitoring: Monitor the volume, type, and source of network traffic to identify any unusual or suspicious activity.
- System log monitoring: Monitor system logs for events that may indicate a security breach, such as failed login attempts or unauthorized access.
- User behavior monitoring: Monitor user activity to identify any unusual patterns or behaviors that may indicate a compromised account.
Once you have established a baseline, you can use it to identify any deviations from normal activity. This can help you to quickly identify potential threats and take action to remediate them.
4. Test, Test, and Test Again
This crucial step involves testing your systems against various cyber threats to identify vulnerabilities and assess the overall resilience of your security infrastructure. The choice of methods you use depends on the specific threats you face and the nature of your systems. Here are some common testing approaches:
- Penetration testing: Also known as pen testing, this simulates a real-world cyberattack by attempting to exploit vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access to your systems. This approach provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of your security controls and identifies areas that may require improvement.
- Social engineering testing: Focuses on evaluating the susceptibility of your employees to manipulation and deception tactics commonly employed by cyber attackers. This testing helps to identify potential weaknesses in user awareness and training, allowing for targeted improvements.
- Physical security testing: Assesses the strength of your physical security measures, such as access control systems, security barriers, and monitoring systems. This testing helps to identify vulnerabilities in physical infrastructure that could be exploited by attackers to gain access to your systems or sensitive data.
- Vulnerability scanning: Involves using automated tools to identify known vulnerabilities in your systems. This testing helps to prioritize remediation efforts and address critical security weaknesses before they can be exploited.
5. Continuously Evaluate and Improve
After identifying and remediating prioritized threats, incorporate the lessons you’ve learned into the security policy. This update should address any gaps in the policy and serve as a valuable learning opportunity for employees. Repeat this process at regular intervals to ensure continuous improvement in cybersecurity posture. Never stop reviewing and evaluating your security policies. Hackers are constantly changing tactics, and so should you.
Cybersecurity is always evolving, and you have to stay vigilant in identifying and addressing threats. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you will help your clients significantly improve their cybersecurity posture and minimize the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.