Since MSPs (managed service providers) handle multiple clients, it’s no surprise why they’re targeted by cyber attackers. Gaining access to an MSP’s systems could allow an attacker access to a wide range of victims.
MSPs are well aware of their vulnerabilities, which is why proactive prevention goes a long way towards staying protected.
According to research by IBM, MSPs are at considerable risk of attack due to compromised credentials through common user software tools like Microsoft Outlook and WordPress. At the same time, cloud service vulnerabilities have tripled, increasing by 200%, giving malicious actors opportunities to exploit these flaws and access their systems.
In this article, we’ll walk through some recent attacks against MSPs and see what can be learned from them. Then, we’ll talk about some potential strategies MSPs can implement now to fortify their defenses.
Recent Attacks Carried Out Against MSPs
If you’re an MSP, you might be wondering how attackers have been gaining access to similar systems. Here are some recent examples to learn from.
CTS Cyber Attack
In 2023, CTS—a MSP providing support to the legal sector in the UK—became the victim of a severe cyberattack as the result of the CitrixBleed vulnerability. The attack disrupted between 80-200 law firms.
Around the same time, IT consulting firm HTC were the victims of a ALPHV ransomware attack that exploited the same vulnerability. Sensitive data—including passports, emails, and confidential documentation—may have been stolen.
Black Hunt Attack
In January, Tigo Business, a market leader in mobile communications, hosting, and cloud services, was impacted by an attack by the ransomware Black Hunt. Over three hundred of Tigo’s services were impacted, and the hackers threatened to sell the data obtained on the dark web. The primary entry point for the attack was unsecured remote desktop protocols (RDPs). The criminals entered the system, cleared the event logs, deleted shadow copies of NTFS records, and terminated the Microsoft Defender program. They were also able to disable the system restore capabilities without users knowing.
Südwestfalen IT Ransomware Attack
Südwestfalen IT, which provides services to more than 70 municipalities in Germany, fell victim to a ransomware attack in 2023, disrupting government services and restricting access to important infrastructure. It’s believed that the Akira ransomware group encrypted their servers, severing data center connections as the company tried to prevent the malware from spreading. The attack occurred at month-end, impacting payments like social assistance and salaries.
Defensive strategies for MSPs
So what can MSPs do now to protect their clients? CISA, a US government agency responsible for cybersecurity and infrastructure protection across all levels of government, has issued advice for MSPs against these threats. As seen in the examples above, malicious actors look for vulnerabilities in devices and software and regularly conduct brute force and phishing attacks in the hopes of infiltrating the victim’s system.
MSPs and their customers need to make every effort to mitigate these attacks through defensive strategies, including:
Network Segmentation and Access Controls
It’s best to limit the number of access points (internet-facing services) that allow controlled entry to the network. Exposing unnecessary services creates additional entry points for attackers. Instead:
- Inventory: Create a complete list of all services accessible from the internet. This includes web servers, email servers, remote access applications, and any other service reachable from the outside world.
- Prioritize ruthlessly: Analyze each service and determine if it’s absolutely essential for your business operations. Can specific functionalities be achieved through internal-only services or secure alternatives?
- Decommission the unnecessary: For services deemed non-critical, disable or completely remove them from your internet-facing infrastructure. This reduces your attack surface and lessens the burden of maintaining and patching them.
- Segregate internal networks: If an attacker breaches a less critical service on the network’s outer segment, they’ll face additional hurdles to reach the more sensitive data stored within isolated segments. This compartmentalization can significantly limit the damage caused by a cyberattack.
- Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Use a two-step verification process to access your organization’s data and applications. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second authentication factor beyond just a password.
- Apply the principle of least privilege: Grant users specific permissions within your organization based on their roles. A data analyst may only need access to specific datasets, while an IT administrator might require broader access for system maintenance. The principle of least privilege applies this concept to user accounts and systems. Grant users and systems only the minimum level of access permissions required for their specific tasks. This minimizes potential damage if an account gets compromised.
Apply Updates Promptly and Scan For Vulnerabilities
Prioritizing installing security updates, especially those addressing known exploited vulnerabilities, is crucial for a strong defense.
CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog identifies vulnerabilities that attackers are actively exploiting. KEV listings are inherently high-risk and should be addressed immediately. Patching these vulnerabilities first significantly reduces the risk of a successful cyberattack. Once a vulnerability is discovered, attackers waste no time developing exploits (tools to take advantage of the weakness). Patching quickly minimizes the window of opportunity attackers have to exploit the vulnerability in your systems.
Vulnerability scanning tools identify weaknesses in your systems and applications before attackers do. This allows you to take corrective action and patch vulnerabilities before they can be used in a cyberattack. New vulnerabilities are discovered all the time. Regular vulnerability scans ensure you stay ahead of the curve and identify new weaknesses promptly. There are various vulnerability scanning tools available, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Choose a reputable tool that can scan your specific systems and applications effectively.
Both MSPs and customers have a role to play in effective patch management and vulnerability scanning.
MSPs managing a customer’s network should prioritize implementing security updates on those systems as quickly as possible. This includes staying informed about KEV listings and patching those vulnerabilities first.
Customers should ensure their MSP has a comprehensive and timely update policy. This policy should outline the process for identifying, prioritizing, and deploying security updates. Customers should also hold their MSPs accountable for adhering to this policy.
Incident Response and Recovery Planning
MSPs should conduct regular backups of critical data and systems, including “golden images” for essential systems. These backups must be stored on separate, offline media to prevent them from being encrypted by ransomware. They must also be routinely tested to ensure they can be restored effectively in case of a cyberattack. If applicable by contract, MSPs should back up customer data regularly and maintain secure offline backups. They must create a comprehensive incident response and recovery plan outlining roles, responsibilities, and procedures for responding to security incidents.
Supply Chain Risk Management
MSPs have to understand their supply chain and assess the security posture of all vendors and third-party suppliers to identify and mitigate potential risks. When entering into contractual agreements, they should clearly define security expectations and responsibilities in contracts with MSPs, including hardening, detection, and incident response.
They must ensure that customers have a thorough understanding of the security services provided so that they can address any gaps in coverage that might impact their cybersecurity defensive posture. Contracts should detail how and when MSPs will notify customers of security incidents impacting their environment.
Additional Measures
These are not the only measures MSPs should take. They should also focus on remote access security through VPN solutions with strong encryption protocols and take care to educate their clients (and their clients’ employees) on how to identify and avoid phishing attacks. In that regard, regular security awareness training can go a long way.
They should also adhere to best practices for password and permission management, including using strong passwords and regularly reviewing access logs.
While none of these measures guarantee that the MSP or their customers won’t face a cyber hack in the future, they will significantly improve their cybersecurity posture and reduce the risk of falling victim to cyberattacks.
Looking ahead
Hackers are exploiting any vulnerability they can to access the networks of MSPs and their clients. But there’s no need to be a victim. By following simple safety guidelines, you can effectively protect your clients and yourself against cyber attacks and breaches.
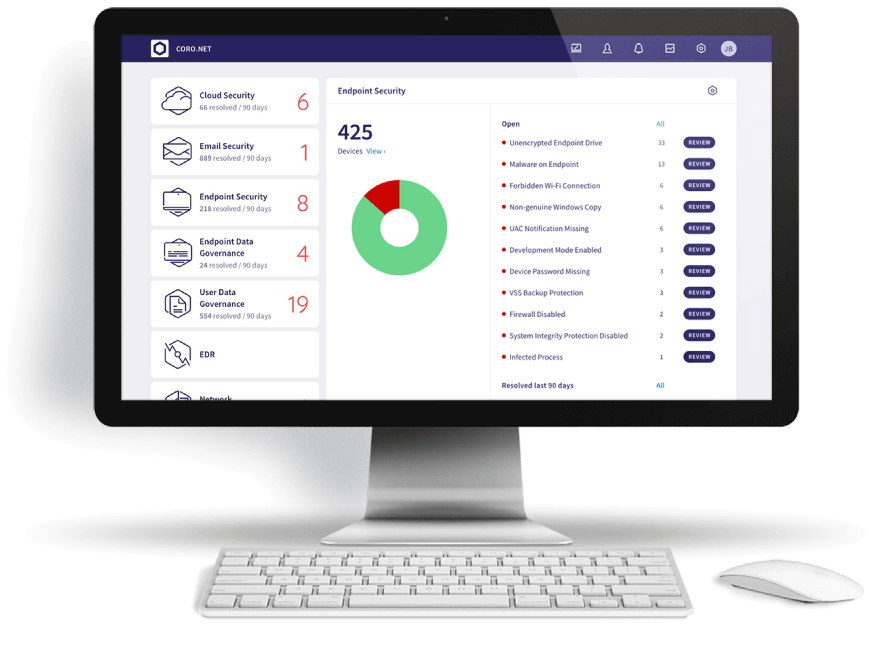
And if you’re looking for a cyber security solution that can protect your systems and those of your clients, Coro can help. Consider partnering with us today.